Explain This Difference in Acid-base Reactivity Between Alcohols and Phenols
The phenoxide ion is stabilized by the delocalization of negative charge due to the resonance in the benzene ring. Basic Properties of Alcohols Alcohols are weak bases similar in strength to water and can accept protons from strong acids to form the conjugate acid called oxonium ions ROH.
Reactions of Alcohols Reaction with Metal.
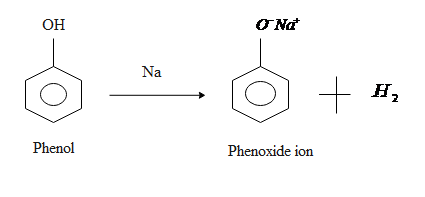
. Compounds like alcohols and phenol which contain an -OH group attached to a hydrocarbon are very weak acids. Because of the greater acidity of phenols phenoxides can be obtained from phenols and aqueous base. When ethanol reacts with sodium metal a base sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas is produced 2ROH Na2RONa H 2.
Halogens such as chlorine or bromine replace the -OH group in an alcohol. Certain tests such as litmus tests ferric chloride tests Lucas test esterification etc can be used to distinguish between alcohol phenol and ether. This reaction the hydrogen ionic was removed from the highly basic hydroxide ion in sodium hydroxide solution.
Phenols are said to be more acidic than aliphatic alcohols in that oxygen electron density is conceived to be delocalized around the ring. Oxidation Reactions of Alcohols. Up to 24 cash back Alkoxides the conjugate bases of alcohols are prepared from alcohols by reaction with reactive metals or metal hydrides.
Alcohols following the elimination of H creates an alkoxide ion which is the. An example is the reaction of methanol with hydrogen bromide to give methyloxonium bromide which is analogous to the formation of hydroxonium bromide from the reaction of hydrogen bromide. Alcohols and phenols are acidic in nature but ethers are not.
Both alcohols and phenols are capable of acting as weakly acidic species. ALCOHOLS THIOLS PHENOLS ETHERS. In contrast weaker bases such as sodium hydroxide can deprotonate phenols.
Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers 2 3 Alcohols 4 The Hydroxy OH Functional Group The hydroxyl group OH is found in the alcohol and phenol functional groups. It acts as a weak acid in water so a solution of phenol will be slightly acidic. This page looks at the reactions of acid anhydrides with water alcohols and phenols including the manufacture of aspirin.
Alcohols and phenols are also weak bases. ROH ZnHCl R-Cl. Difference Between Alcohol and Phenol.
ArOHaq NaOHaq ArONaaq H 2 O. When an alcohol is treated with sodium hydroxide the following acid-base equilibrium occurs. Phenols on the other hand are organic compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group which is attached to an aromatic system of hydrocarbons arene.
There are aliphatic and aromatic compounds in organic. However this image suggests that in fact the inductive effect is responsible for a great deal of phenols additional acidity. The difference in boiling points is as much as 153 o.
Phenols react with aqueous sodium hydroxide to produce phenoxide ions. Some Commercially Important Alcohols. The key difference between alcohols and phenols is that the alcohols are organic compounds containing OH group as an essential component whereas the phenols are a group of alcohols which contains OH group and a benzene ring as essential components.
Alcohols are typically not acidic enough to be deprotonated without the use of strong bases such as Grignard reagents or organolithium reagents. Nevertheless it does some give some clue to explain the REACTIVITY of phenols. October 28 2011 Posted by Madhu.
Alcohol a stronger acid by stabilizing the conjugate base alkoxide 85 Phenols are much more acidic than aliphatic alcohols. The phenol is no exception - the only difference is the slow reaction because phenol is such a weak acid. Alcohol Alkoxide R OH Alcohol H X 2 O R O X.
No Reaction S N 1 Reduction of Acids Esters Aldehydes and Ketones The carbonyl group of several functional groups may be converted to the alcohol by reducing agents. All alcohols phenols and ethers are soluble in water because of their ability to form intermolecular hydrogen bonding with water. Acids react with more reactive metals to give hydrogen gas.
Phenols differ from alcohols in that they are slightly acidic in water. Ionization of alcohols is represented by the following equilibrium. This can be explained as follows.
They react with aqueous sodium hydroxide NaOH to form salts. The difference in the acidic character of phenols and alcohol is due to the difference in reactivity of these compounds towards the ionization of the OH bond. Explain this difference in acid- base reactivity between alcohols and phenols.
The alcohols are a class of organic compounds that hold at least one hydroxyl functional group that is attached to a carbon atom. This is yet another example of how leaving group stability often influences the rate of a reaction. They are used as organic bases.
Phenol is somewhat soluble in water. In phenols OH is connected to a benzene ring. As we can see in the picture immediately above it seems that the sp 2 carbon.
Shown below each alcohol. Simple 1º and 2º-alcohols in the gaseous state lose hydrogen when exposed to a hot copper surface. Phenol is heated in a dry tube When it is not melted and a small piece of.
R 2 C-OH alcohol HCl. This approach may be a bit simplistic and wrong-headed reduced charge density of the phenoxide seems to be the determinant. But I disagree that phenols and alcohols have nearly no reactions in common.
Thats not the same as hydroxide OH- which is ionic in alcohols a hydroxyl group is connected to a carbon atom. Oxidation Alcohols can be oxidized by oxidizing agents such as chromate or dichromate. They can be protonated on the oxygen by strong.
This catalytic dehydrogenation reaction produces aldehydes as shown below and ketones and since the carbon atom bonded to the oxygen is oxidized such alcohol to carbonyl conversions are. These reactions are all considered together because their chemistry is so similar. However phenol is sufficiently acidic for it to have recognisably acidic properties - even if it is still a very weak acid.
Alcohols are so weakly acidic that for normal lab purposes their acidity can be virtually ignored. Alcohols do not undergo such base-induced elimination reactions and are in fact often used as solvents for such reactions. There is also a great similarity between acid anhydrides and acyl chlorides acid chlorides as far as these reactions are concerned.
As the hydrocarbon part of an alcohol gets larger the alcohol becomes less water soluble and more soluble in nonpolar solvents. When deprotonated their conjugate bases are both strong bases and good nucleophiles. A benzene ring is generally considered electron withdrawing inductive effect the benzene ring stabilizes the negative charge of the phenoxide ion through resonance Fig.
A lot of people rationalize the acidity of phenol by saying that resonance is responsible for much of phenols acidity as opposed to aliphatic alcohols. This indicates that the acidity of phenols is higher in comparison to the alcohols. And they can undergo many reactions in common at oxygen such as alkylation silylation acylation and many others.
What Is The Distinguish Test Between Alcohol And Phenol Quora

Physical Properties Of Alcohol Phenols And Ethers Concepts Video Q A
Explain Why Phenol Is More Acidic Than Ethanol Class 12 Chemistry Cbse
No comments for "Explain This Difference in Acid-base Reactivity Between Alcohols and Phenols"
Post a Comment